Mybatis Plus
MyBatis-Plus(简称 MP)是一个 MyBatis 的增强工具,在 MyBatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生。
【尚硅谷】2022版MyBatisPlus教程(一套玩转mybatis-plus)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
- 无侵入、损耗小、强大的CRUD操作
- 支持Lambda形式调用,支持多种数据库
- 支持主键自动生成,支持ActiveRecord模式
- 支持自定义全局通用操作,支持关键词自动转义
- 内置代码生成器、内置分页插件、内置性能分析插件
- 内置全局拦截插件、内置SQL注入剥离器
BaseMapper
public interface BaseMapper<T> extends Mapper<T> {
int insert(T entity);
int deleteById(Serializable id);
int deleteByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap);
int delete(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
int deleteBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
int updateById(@Param("et") T entity);
int update(@Param("et") T entity, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> updateWrapper);
T selectById(Serializable id);
List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param("coll") Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
List<T> selectByMap(@Param("cm") Map<String, Object> columnMap);
T selectOne(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
Integer selectCount(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<T> selectList(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<Map<String, Object>> selectMaps(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
List<Object> selectObjs(@Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
<E extends IPage<T>> E selectPage(E page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
<E extends IPage<Map<String, Object>>> E selectMapsPage(E page, @Param("ew") Wrapper<T> queryWrapper);
}CURD
使用mapper继承BaseMapper<T>即可开箱即用
@Test
void TestInsert(){
user user = new user();
user.setId(880);
user.setAccount("天天学习");
user.setPassword("hhh");
int res = UserMapper.insert(user);
System.out.println(res);
}
@Test
void TestDelete(){
// 一:
// int res = UserMapper.deleteById(1);
// System.out.println(res);
// 二:
// delete from user where account = ? and password = ?
// HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// map.put("account","jkl");
// map.put("password","123root");
// UserMapper.deleteByMap(map);
// 三:
// 删除多个
// DELETE FROM user WHERE id IN ( ? , ? )
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(80,880);
UserMapper.deleteBatchIds(list);
}
@Test
void TestUpdata(){
user user = new user();
user.setAccount("改了");
UpdateWrapper<user> q = new UpdateWrapper<>();
q.eq("password","666");
// 不屑password 不被修改
UserMapper.update(user,q);
}
@Test
void TestSelect(){
// 通过id查询信息
// user user = UserMapper.selectById(2);
// System.out.println(user.toString().isEmpty());
// 通过多个id进行查询
// List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(3,2);
// List<user> users = UserMapper.selectBatchIds(list);
// users.forEach(System.out::println);
// 通过map查询
// HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// map.put("account",666);
// List<user> users = UserMapper.selectByMap(map);
// users.forEach(System.out::println);
// 所有的数据
// List<user> users = UserMapper.selectList(null);
// users.forEach(System.out::println);
}wapper条件构造器
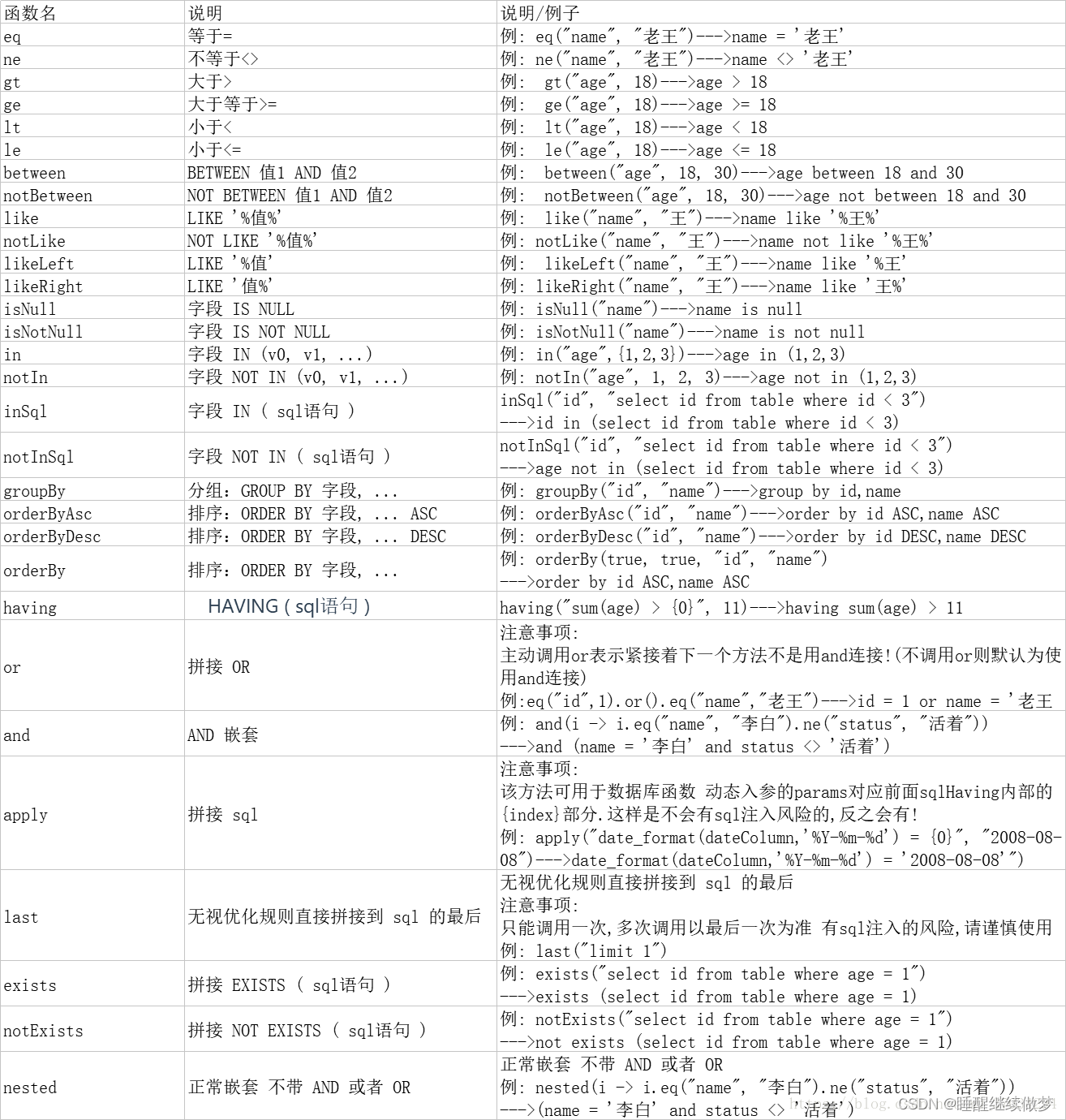
注解说明
@TableName 表名
@TableId 主键
---@TableId(type= IdType.AUTO) 自增
---@TableId(type= IdType.NONE) 雪花算法 赋值
@TableField 把表中字段和实体类对应
---@TableField(value="name") 映射
---@TableField(exist=false) 不是数据库中字段
---@TableField(select = false) 不会参与查询 返回值为null
MybatisX
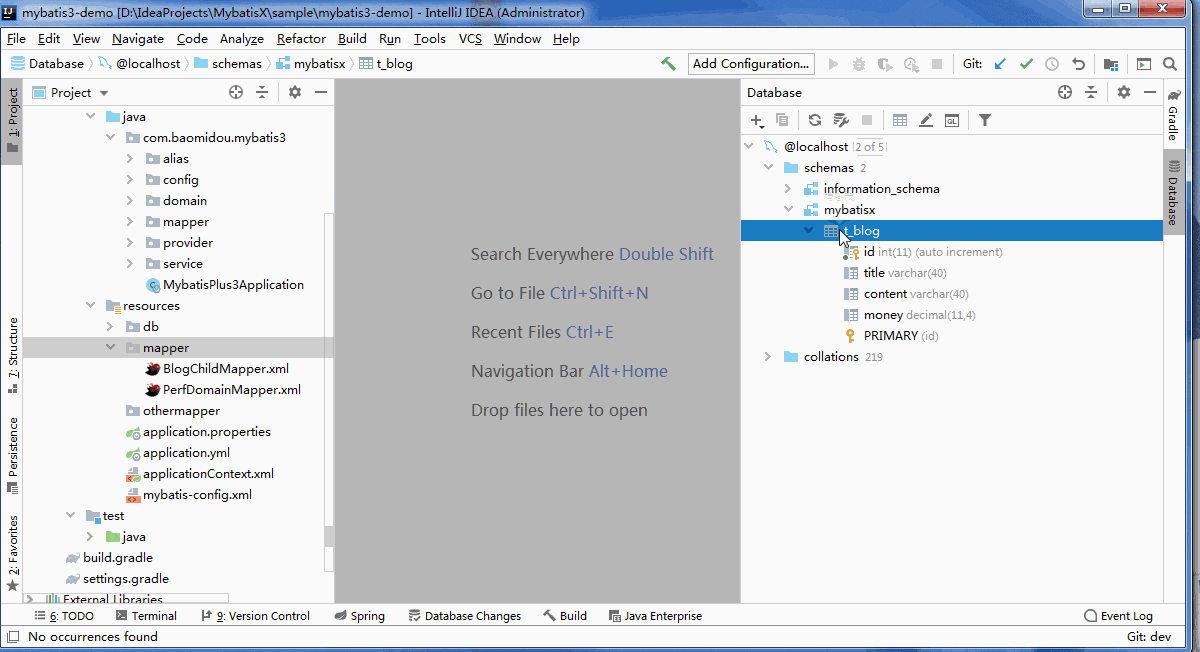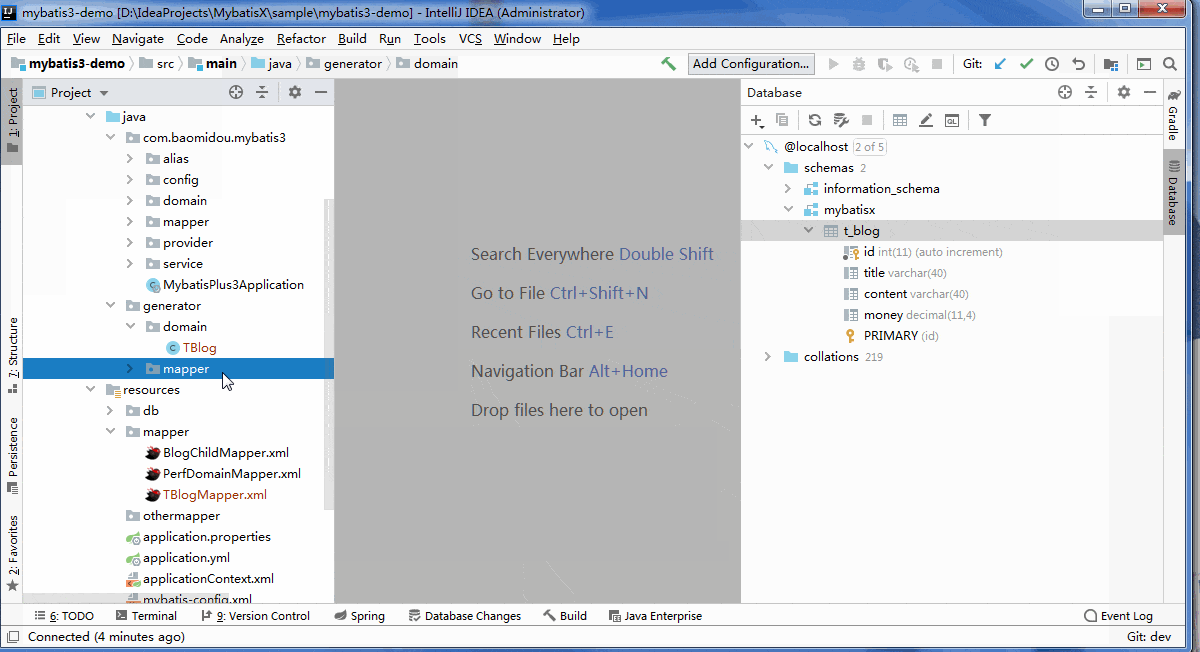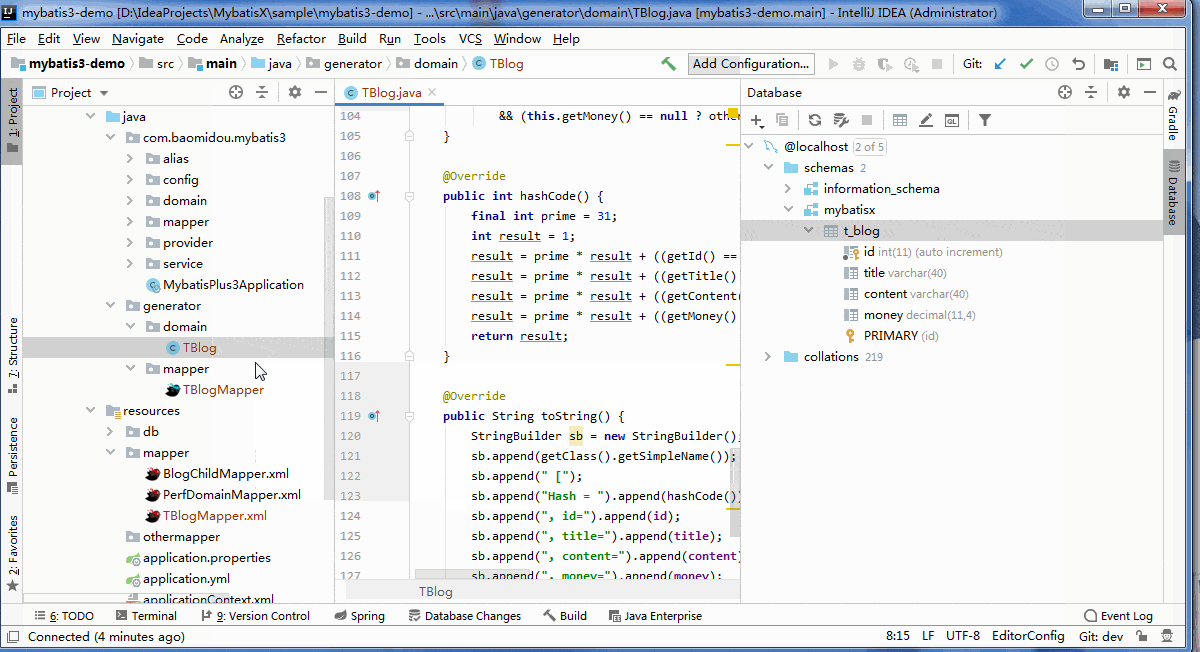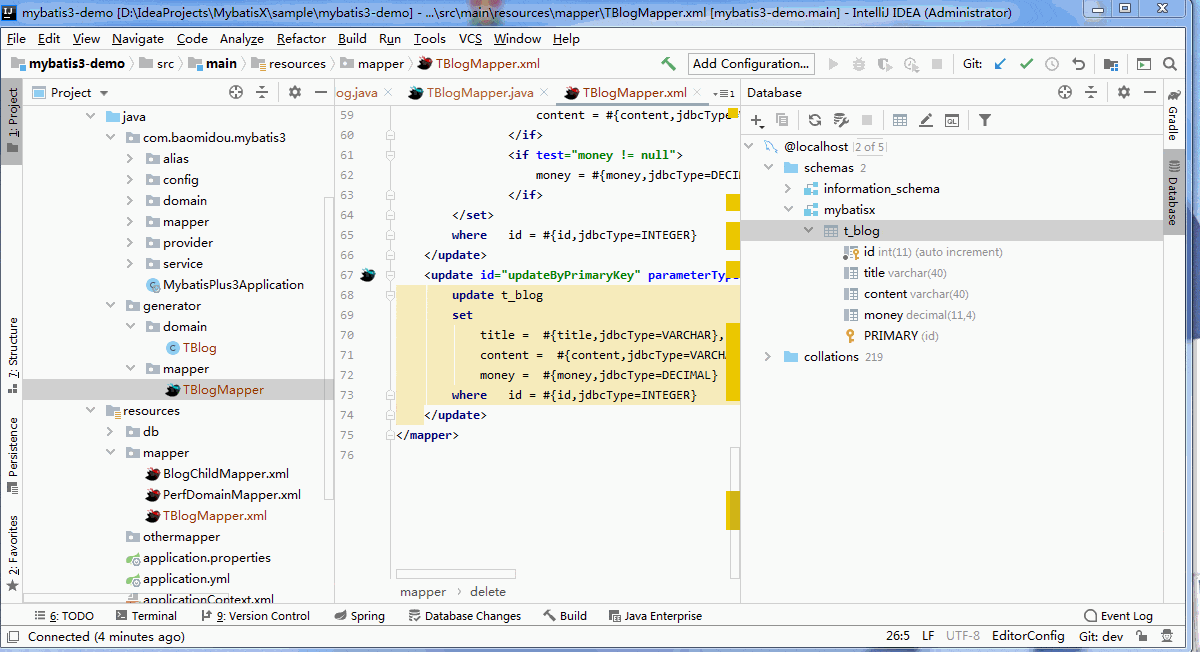
分页
- config
@Configuration
public class MybatisConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor(){
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(new PaginationInnerInterceptor(DbType.MYSQL));
return interceptor;
}
}- 使用
@Override
public JSONObject userList(Integer page) {
IPage<Record> recordIPage = new Page<>(page,10);
QueryWrapper<Record> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.orderByAsc("id");
List<Record> list = recordMapper.selectPage(recordIPage,queryWrapper).getRecords();
JSONObject resp = new JSONObject();
resp.put("records",list);
resp.put("count",recordMapper.selectCount(null));
return resp;
}Mybatis+字段+1
UpdateWrapper<article> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
updateWrapper.setSql("up = up + 1").eq("id",21);
System.out.println(articleMapper.update(null, updateWrapper)); LambdaUpdateWrapper<article> q = new LambdaUpdateWrapper<>();
q.setSql("up = up + 1");
q.setSql("views = views + 1");
q.eq(article::getId,22);
System.out.println(articleMapper.update(null, q));事务
测试时加入@Transactional 不会改变数据,不会污染数据,不管如何都会回滚
事务主要的作用体现在以下几个方面:
数据一致性:事务可以确保多个操作在一个逻辑单元中执行,要么全部执行成功,要么全部失败回滚。在多个操作之间存在依赖关系的情况下,事务可以确保数据的一致性,防止数据冲突和数据丢失等问题。
错误回滚:事务可以在发生错误或异常时回滚到之前的状态,保证数据的完整性。如果在多个操作中发生了错误,事务会自动将所有操作撤消,将数据回滚至操作之前的状态。
并发控制:事务可以解决数据库并发访问的问题。当多个用户同时对同一数据进行操作时,事务可以通过锁机制来控制这些操作的执行顺序,以避免并发访问引起的数据冲突和错误。
提高性能:事务可以优化数据库操作的性能。如果在多个操作中涉及到较多的I/O操作或网络传输,将所有操作合并到一个事务中可以减少I/O操作和网络传输,提高数据库操作的性能。
因此,事务对于确保数据的正确性、完整性和一致性非常重要,是保证数据库安全和稳定运行的基本手段。
默认形况下、只有出现RuntimeException才回滚异常。rollbackFor属性用于控制出现何种异常类型,回滚事务。@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)任何异常都回滚
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public boolean addUser(User user) {
try {
// 添加用户
userMapper.insert(user);
// 手动抛出异常,模拟事务回滚
throw new RuntimeException("添加用户时出现异常");
} catch (Exception e) {
// 捕获异常,并打印异常信息
e.printStackTrace();
// 抛出运行时异常,使事务回滚
throw new RuntimeException("添加用户时出现异常");
}
}
}更新日志
6f732-于ded7f-于3a085-于9fd8e-于1ea7d-于4655f-于a0e4c-于ae286-于ad8f4-于0b901-于1da05-于0f5ff-于331b9-于